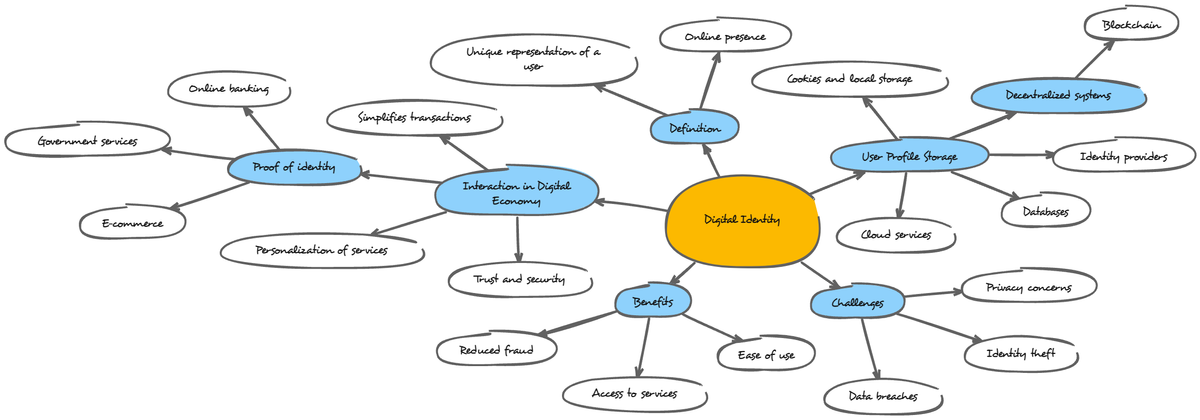
Digital Identity
Online Presence
- Online Banking: Conducting banking transactions electronically through a bank's website or app.
- E-commerce: Buying and selling goods or services over the internet.
- Government Services: Accessing government services such as renewing passports, applying for benefits, or filing taxes online.
Digital Identity
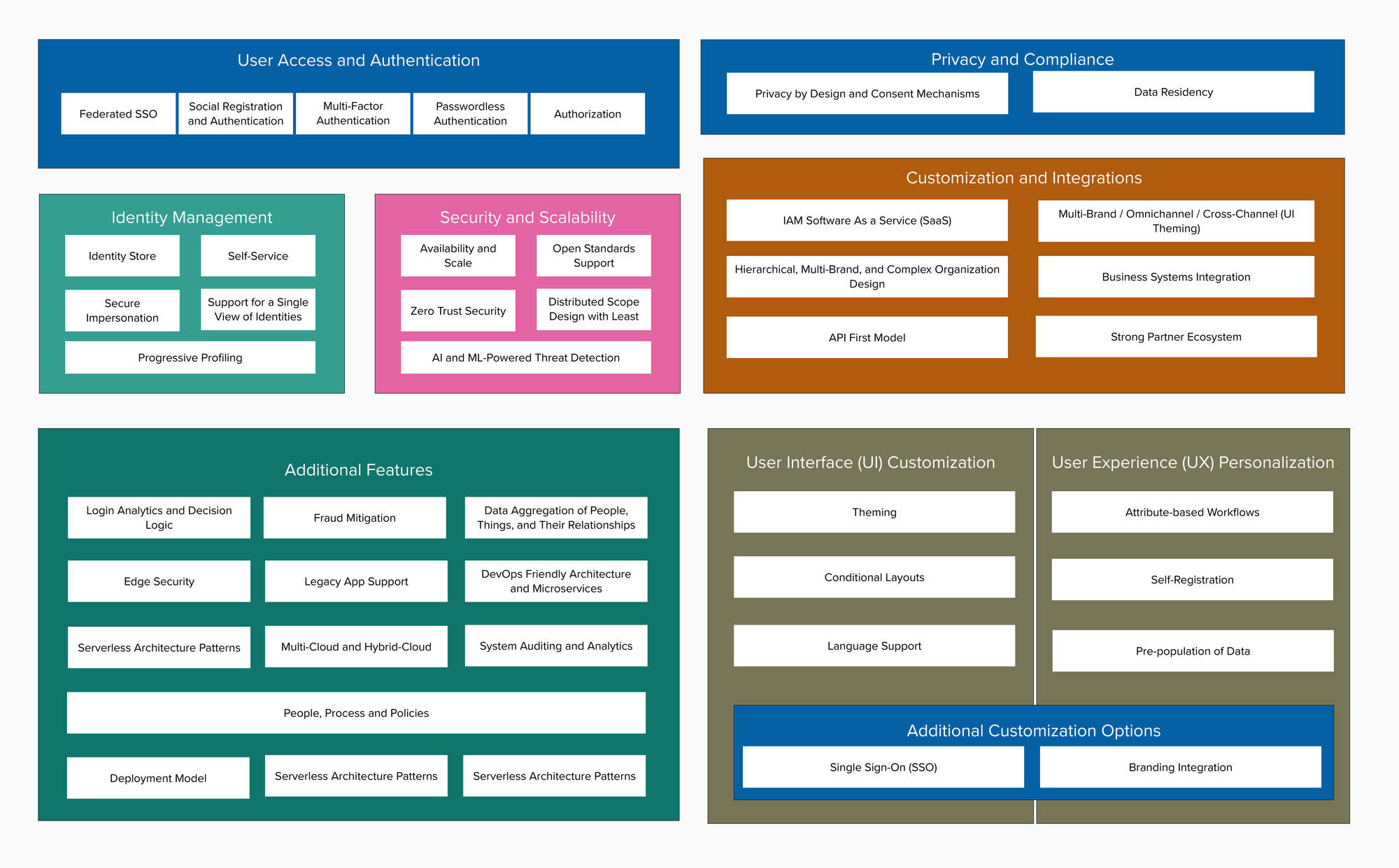
- Unique representation of a person online: A digital identity is a collection of attributes that uniquely identify a person online. It can include things like a username, email address, profile information on social media sites, and online purchase history.
- Benefits:
- Convenience: Enables easier access to online services and simplifies transactions.
- Personalization of services: Allows websites and applications to tailor their offerings to your individual needs and preferences.
- Challenges:
- Privacy concerns: Collection and use of personal data for digital identities raises privacy concerns.
- Security risks: Digital identities can be vulnerable to hacking and identity theft.
Definition
- Online presence: A person's or organization's visibility on the internet. This can include websites, social media profiles, online listings, and other digital content.
Interaction in Digital Economy
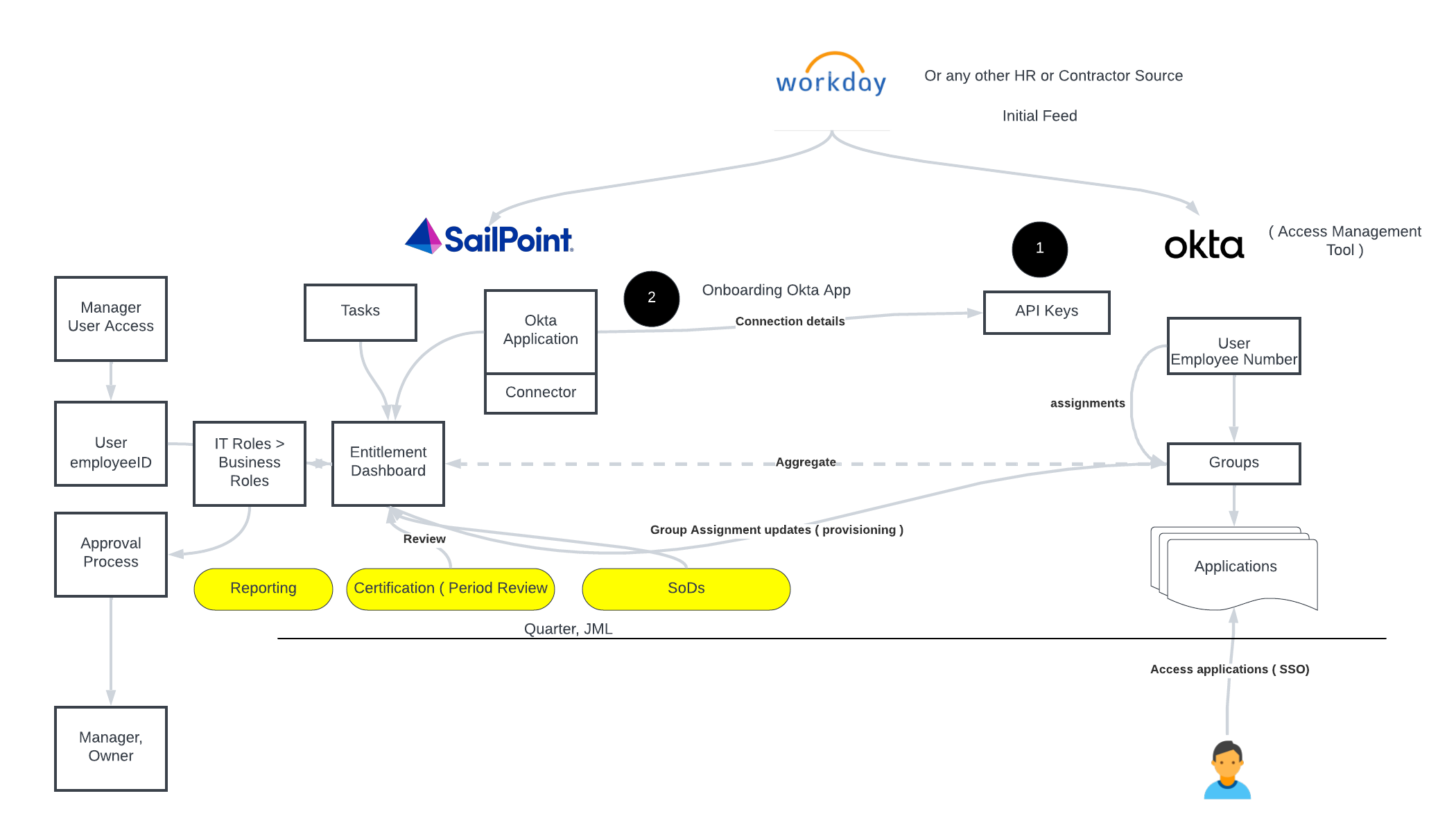
- Proof of identity: Verifying your identity online is crucial for many activities, such as accessing online accounts, making online purchases, or using government services.
- Trust and security: Security measures are necessary to ensure the trustworthiness of online interactions and protect personal information.
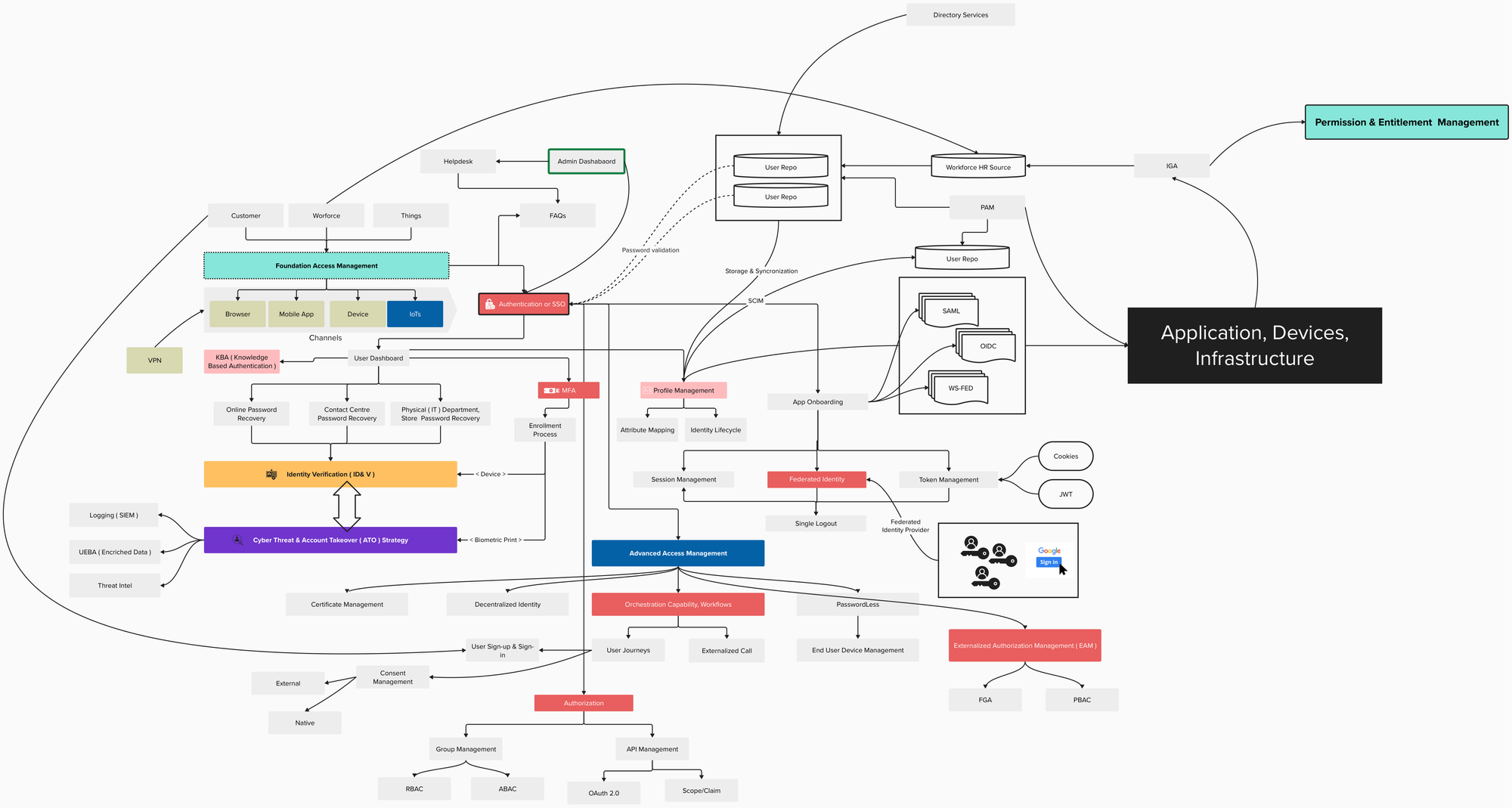
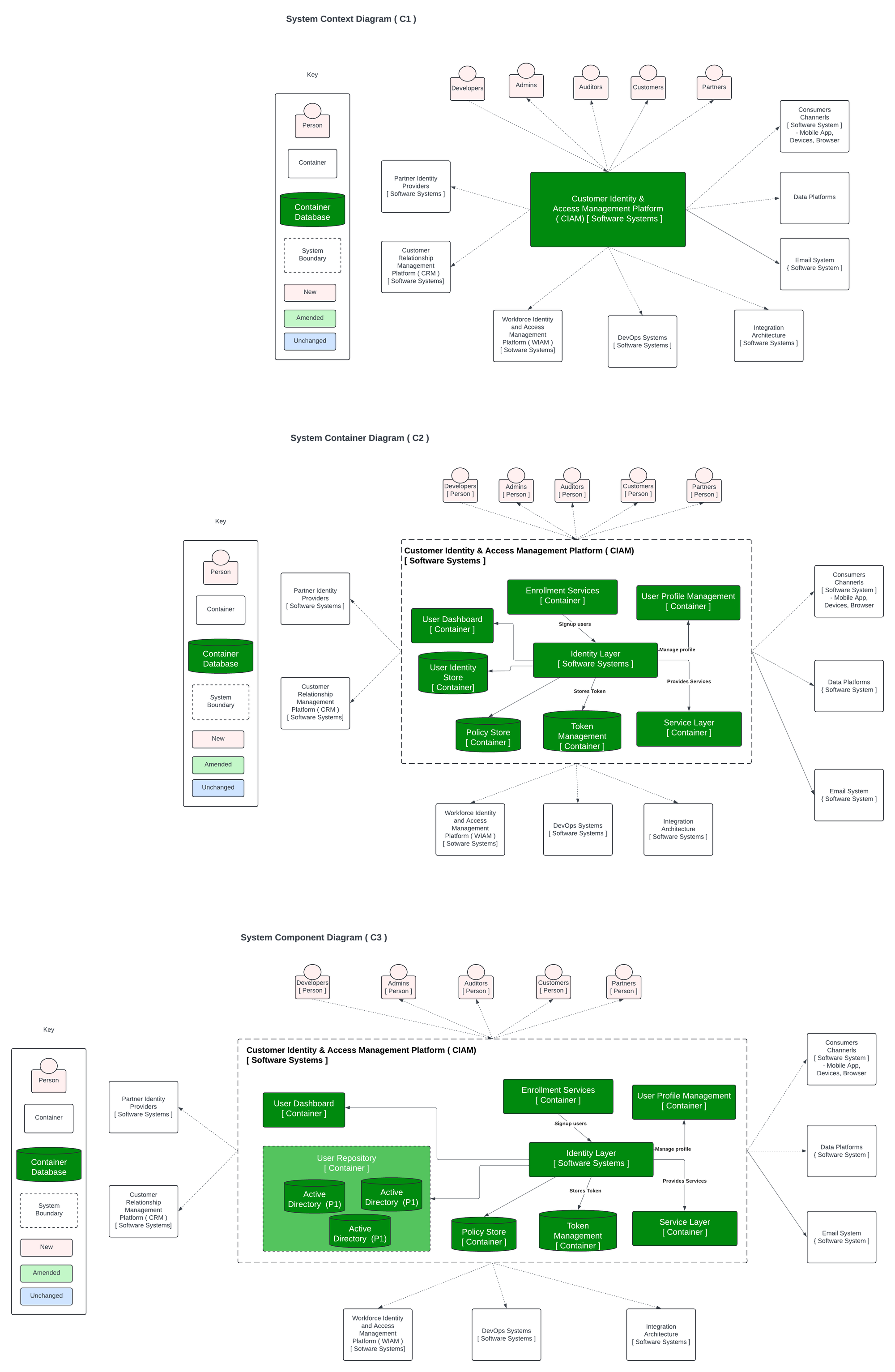
Components
- User Profile Storage: Where your personal information and profile data is stored online. This could be on social media platforms, e-commerce websites, or cloud storage services.
- Databases: Large collections of structured data used to store and manage information relevant to digital identities.
- Cloud Services: Companies that provide access to computing resources, storage, and software over the internet.
Authentication
- Simplifies transactions: Authentication methods allow for secure online transactions by verifying a user's identity.
- Types of Authentication: The image lists various methods for verifying a user's identity online, including:
- Password-based authentication
- Biometric authentication (fingerprint, facial recognition, iris scan)
- Token-based authentication (smart cards, USB tokens)
- Knowledge-based authentication (security questions, PINs)
- Location-based authentication (geofencing)
- Time-based authentication (OTP - One-Time Passwords)
Privacy
- Cookies and local storage: Technologies that websites use to store data locally on a user's device. This data can be used to track user activity and personalize the user experience, but it also raises privacy concerns.
Decentralized Systems
- Blockchain: A distributed ledger technology that allows for secure, transparent, and tamper-proof recording of transactions. Blockchain has the potential to revolutionize digital identity management by creating a more secure and user-controlled way to store and share identity data.